mirror of
https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips.git
synced 2026-02-01 06:48:51 +00:00
Compare commits
2 Commits
inbox-mode
...
nips/302
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
0dd66f0661 | ||
|
|
3bbbe3ad71 |
2
07.md
2
07.md
@@ -20,8 +20,6 @@ Aside from these two basic above, the following functions can also be implemente
|
||||
async window.nostr.getRelays(): { [url: string]: {read: boolean, write: boolean} } // returns a basic map of relay urls to relay policies
|
||||
async window.nostr.nip04.encrypt(pubkey, plaintext): string // returns ciphertext and iv as specified in nip-04 (deprecated)
|
||||
async window.nostr.nip04.decrypt(pubkey, ciphertext): string // takes ciphertext and iv as specified in nip-04 (deprecated)
|
||||
async window.nostr.nip44.encrypt(pubkey, plaintext): string // returns ciphertext as specified in nip-44
|
||||
async window.nostr.nip44.decrypt(pubkey, ciphertext): string // takes ciphertext as specified in nip-44
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Implementation
|
||||
|
||||
7
18.md
7
18.md
@@ -20,10 +20,9 @@ reposted.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quote Reposts
|
||||
|
||||
Quote reposts are `kind 1` events with an embedded `q` tag of the note being
|
||||
quote reposted. The `q` tag ensures quote reposts are not pulled and included
|
||||
as replies in threads. It also allows you to easily pull and count all of the
|
||||
quotes for a post.
|
||||
Quote reposts are `kind 1` events with an embedded `e` tag
|
||||
(see [NIP-08](08.md) and [NIP-27](27.md)). Because a quote repost includes
|
||||
an `e` tag, it may show up along replies to the reposted note.
|
||||
|
||||
## Generic Reposts
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
197
29.md
197
29.md
@@ -1,197 +0,0 @@
|
||||
NIP-29
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Relay-based Groups
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
`draft` `optional`
|
||||
|
||||
This NIP defines a standard for groups that are only writable by a closed set of users. They can be public for reading by external users or not.
|
||||
|
||||
Groups are identified by a random string of any length that serves as an _id_.
|
||||
|
||||
There is no way to create a group, what happens is just that relays (most likely when asked by users) will create rules around some specific ids so these ids can serve as an actual group, henceforth messages sent to that group will be subject to these rules.
|
||||
|
||||
Normally a group will originally belong to one specific relay, but the community may choose to move the group to other relays or even fork the group so it exists in different forms -- still using the same _id_ -- across different relays.
|
||||
|
||||
## Relay-generated events
|
||||
|
||||
Relays are supposed to generate the events that describe group metadata and group admins. These are parameterized replaceable events signed by the relay keypair directly, with the group _id_ as the `d` tag.
|
||||
|
||||
## Group identifier
|
||||
|
||||
A group may be identified by a string in the format `<host>'<group-id>`. For example, a group with _id_ `abcdef` hosted at the relay `wss://groups.nostr.com` would be identified by the string `groups.nostr.com'abcdef`.
|
||||
|
||||
## The `h` tag
|
||||
|
||||
Events sent by users to groups (chat messages, text notes, moderation events etc) must have an `h` tag with the value set to the group _id_.
|
||||
|
||||
## Timeline references
|
||||
|
||||
In order to not be used out of context, events sent to these groups may contain references to previous events seen from the same relay in the `previous` tag. The choice of which previous events to pick belongs to the clients. The references are to be made using the first 8 characters (4 bytes) of any event in the last 50 events seen by the user in the relay, excluding events by themselves. There can be any number of references (including zero), but it's recommended that clients include at least 3 and that relays enforce this.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a hack to prevent messages from being broadcasted to external relays that have forks of one group out of context. Relays are expected to reject any events that contain timeline references to events not found in their own database. Clients should also check these to keep relays honest about them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Late publication
|
||||
|
||||
Relays should prevent late publication (messages published now with a timestamp from days or even hours ago) unless they are open to receive a group forked or moved from another relay.
|
||||
|
||||
## Event definitions
|
||||
|
||||
- *text root note* (`kind:11`)
|
||||
|
||||
This is the basic unit of a "microblog" root text note sent to a group.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
"kind": 11,
|
||||
"content": "hello my friends lovers of pizza",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["h", "<group-id>"],
|
||||
["previous", "<event-id-first-chars>", "<event-id-first-chars>", ...]
|
||||
]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- *threaded text reply* (`kind:12`)
|
||||
|
||||
This is the basic unit of a "microblog" reply note sent to a group. It's the same as `kind:11`, except for the fact that it must be used whenever it's in reply to some other note (either in reply to a `kind:11` or a `kind:12`). `kind:12` events SHOULD use NIP-10 markers, leaving an empty relay url:
|
||||
|
||||
* `["e", "<kind-11-root-id>", "", "root"]`
|
||||
* `["e", "<kind-12-event-id>", "", "reply"]`
|
||||
|
||||
- *chat message* (`kind:9`)
|
||||
|
||||
This is the basic unit of a _chat message_ sent to a group.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
"kind": 9,
|
||||
"content": "hello my friends lovers of pizza",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["h", "<group-id>"],
|
||||
["previous", "<event-id-first-chars>", "<event-id-first-chars>", ...]
|
||||
]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- *chat message threaded reply* (`kind:10`)
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to `kind:12`, this is the basic unit of a chat message sent to a group. This is intended for in-chat threads that may be hidden by default. Not all in-chat replies MUST use `kind:10`, only when the intention is to create a hidden thread that isn't part of the normal flow of the chat (although clients are free to display those by default too).
|
||||
|
||||
`kind:10` SHOULD use NIP-10 markers, just like `kind:12`.
|
||||
|
||||
- *join request* (`kind:9021`)
|
||||
|
||||
Any user can send one of these events to the relay in order to be automatically or manually added to the group. If the group is `open` the relay will automatically issue a `kind:9000` in response adding this user. Otherwise group admins may choose to query for these requests and act upon them.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 9021,
|
||||
"content": "optional reason",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["h", "<group-id>"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- *moderation events* (`kinds:9000-9020`) (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
Clients can send these events to a relay in order to accomplish a moderation action. Relays must check if the pubkey sending the event is capable of performing the given action. The relay may discard the event after taking action or keep it as a moderation log.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 90xx,
|
||||
"content": "optional reason",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["h", "<group-id>"],
|
||||
["previous", ...]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each moderation action uses a different kind and requires different arguments, which are given as tags. These are defined in the following table:
|
||||
|
||||
| kind | name | tags |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| 9000 | `add-user` | `p` (pubkey hex) |
|
||||
| 9001 | `remove-user` | `p` (pubkey hex) |
|
||||
| 9002 | `edit-metadata` | `name`, `about`, `picture` (string) |
|
||||
| 9003 | `add-permission` | `p` (pubkey), `permission` (name) |
|
||||
| 9004 | `remove-permission` | `p` (pubkey), `permission` (name) |
|
||||
| 9005 | `delete-event` | `e` (id hex) |
|
||||
| 9006 | `edit-group-status` | `public` or `private`, `open` or `closed` |
|
||||
|
||||
- *group metadata* (`kind:39000`) (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
This event defines the metadata for the group -- basically how clients should display it. It must be generated and signed by the relay in which is found. Relays shouldn't accept these events if they're signed by anyone else.
|
||||
|
||||
If the group is forked and hosted in multiple relays, there will be multiple versions of this event in each different relay and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 39000,
|
||||
"content": "",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["d", "<group-id>"],
|
||||
["name", "Pizza Lovers"],
|
||||
["picture", "https://pizza.com/pizza.png"],
|
||||
["about", "a group for people who love pizza"],
|
||||
["public"], // or ["private"]
|
||||
["open"] // or ["closed"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`name`, `picture` and `about` are basic metadata for the group for display purposes. `public` signals the group can be _read_ by anyone, while `private` signals that only AUTHed users can read. `open` signals that anyone can request to join and the request will be automatically granted, while `closed` signals that members must be pre-approved or that requests to join will be manually handled.
|
||||
|
||||
- *group admins* (`kind:39001`) (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the group metadata, this event is supposed to be generated by relays that host the group.
|
||||
|
||||
Each admin gets a label that is only used for display purposes, and a list of permissions it has are listed afterwards. These permissions can inform client building UI, but ultimately are evaluated by the relay in order to become effective.
|
||||
|
||||
The list of capabilities, as defined by this NIP, for now, is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- `add-user`
|
||||
- `edit-metadata`
|
||||
- `delete-event`
|
||||
- `remove-user`
|
||||
- `add-permission`
|
||||
- `remove-permission`
|
||||
- `edit-group-status`
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 39001,
|
||||
"content": "list of admins for the pizza lovers group",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["d", "<group-id>"],
|
||||
["p", "<pubkey1-as-hex>", "ceo", "add-user", "edit-metadata", "delete-event", "remove-user"],
|
||||
["p", "<pubkey2-as-hex>", "secretary", "add-user", "delete-event"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- *group members* (`kind:39002`) (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to *group admins*, this event is supposed to be generated by relays that host the group.
|
||||
|
||||
It's a NIP-51-like list of pubkeys that are members of the group. Relays might choose to not to publish this information or to restrict what pubkeys can fetch it.
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 39002,
|
||||
"content": "list of members for the pizza lovers group",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["d", "<group-id>"],
|
||||
["p", "<admin1>"],
|
||||
["p", "<member-pubkey1>"],
|
||||
["p", "<member-pubkey2>"],
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Storing the list of groups a user belongs to
|
||||
|
||||
A definition for kind `10009` was included in [NIP-51](51.md) that allows clients to store the list of groups a user wants to remember being in.
|
||||
59
302.md
Normal file
59
302.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
NIP-302
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
Relay Pools
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
`draft` `optional`
|
||||
|
||||
# Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
This NIP introduces a system for the creation, management, and utilization of relay pools.
|
||||
|
||||
# Specification
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating a Relay Pool
|
||||
|
||||
Users initiate a relay pool by creating a Nostr event with `kind` 30010.
|
||||
- The `content` field is the description of the relay pool.
|
||||
- A `d` tag has the name of the relay pool (e.g. awesome-pool) as value.
|
||||
- At least one `r` tag MUST be present with the third value as `"pool"`. These pool addresses are URLs clients can connect to.
|
||||
- Zero or more `r` tags with third value as `"member"`, empty string, or missing signify a relay pool member.
|
||||
- Zero or more `auth-required` tags with one of the following values: `nip-42` or `nip-98`. Clients wishing to connect to Relay Pools with an `auth-required` tag MUST support at least one of the NIPs before initiating a connection.
|
||||
|
||||
## Updating the Relay Pool
|
||||
|
||||
To update the relay member list of a relay pool, pool addresses, a new event of kind 30010 with the same `d` tag MUST be published.
|
||||
Pool addresses and member relays are added or removed at any time.
|
||||
|
||||
## Joining a Relay Pool
|
||||
|
||||
Relay operators wishing to join a relay pool publish a Relay Pool Join Request event with `kind` 8000:
|
||||
- `p` tag referencing the pubkey of the Relay Pool (event kind 30010).
|
||||
- `a` tag addressing the kind 30010 event.
|
||||
- a single `r` tag with the relay address (e.g., wss://cool-relay.cool-domain.com).
|
||||
|
||||
## Inclusion in the Relay Pool
|
||||
|
||||
Relay Pool Operators MAY include new member relays by updating the Relay Pool event and adding their `r` tag from the kind 8000 event.
|
||||
|
||||
### Leaving a Relay Pool
|
||||
|
||||
Member Relay Operators can request removal from a relay pool by publishing an Event Deletion (kind 5) referencing their Relay Pool Join Request event (kind 8000).
|
||||
Upon receiving a kind 5 event, the Relay Pool Operator SHOULD issue a new event of kind 30010, removing the `r` tag that references the parting relay.
|
||||
|
||||
# Verification
|
||||
|
||||
Relay Pool Operators MAY require further steps as part of the application process (e.g. proof of work (mined event), payment or out-of-channel communication).
|
||||
Relay Pool Operators MAY respond with kind 1 note to Relay Pool Join Requests events by referencing the event kind 8000 and/or tagging the requester's pubkey.
|
||||
A Relay Pool is only successfully joined once a new Relay Pool event is published including the `r` tag from the Relay Pool Join Request.
|
||||
|
||||
# Client Connection
|
||||
|
||||
Clients can discover relay pools by subscribing to events of kind 30010.
|
||||
Clients MUST connect directly to the relay pool addresses in order to be routed to member relays.
|
||||
Relay Pools SHOULD distribute client connections among Relay Pool Members using a fair algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
## Proxying and Authentication
|
||||
Relay Pools MAY serve incoming WebSockets connections either by passthrough or by redirect.
|
||||
Relay Pools that require authentication (e.g. for paid relay pools) MUST support either [NIP-42](42.md), [NIP-98](98.md) or both.
|
||||
102
34.md
102
34.md
@@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
NIP-34
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
`git` stuff
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
`draft` `optional`
|
||||
|
||||
This NIP defines all the ways code collaboration using and adjacent to [`git`](https://git-scm.com/) can be done using Nostr.
|
||||
|
||||
## Repository announcements
|
||||
|
||||
Git repositories are hosted in Git-enabled servers, but their existence can be announced using Nostr events, as well as their willingness to receive patches, bug reports and comments in general.
|
||||
|
||||
```jsonc
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 30617,
|
||||
"content": "",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["d", "<repo-id>"],
|
||||
["name", "<human-readable project name>"],
|
||||
["description", "brief human-readable project description>"],
|
||||
["web", "<url for browsing>", ...], // a webpage url, if the git server being used provides such a thing
|
||||
["clone", "<url for git-cloning>", ...], // a url to be given to `git clone` so anyone can clone it
|
||||
["relays", "<relay-url>", ...] // relays that this repository will monitor for patches and issues
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tags `web`, `clone`, `relays` can have multiple values.
|
||||
|
||||
Except `d`, all tags are optional.
|
||||
|
||||
## Patches
|
||||
|
||||
Patches can be sent by anyone to any repository. Patches to a specific repository SHOULD be sent to the relays specified in that repository's announcement event's `"relays"` tag. Patch events SHOULD include an `a` tag pointing to that repository's announcement address.
|
||||
|
||||
```jsonc
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 1617,
|
||||
"content": "<patch>", // contents of <git format-patch>
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["a", "30617:<base-repo-owner-pubkey>:<base-repo-id>"],
|
||||
["p", "<repository-owner>"],
|
||||
["p", "<other-user>"], // optionally send the patch to another user to bring it to their attention
|
||||
|
||||
// for the first patch in a thread or series
|
||||
["t", "root"],
|
||||
|
||||
// optional tags for when it is desirable that the merged patch has a stable commit id
|
||||
// these fields are necessary for ensuring that the commit resulting from applying a patch
|
||||
// has the same id as it had in the proposer's machine -- all these tags can be omitted
|
||||
// if the maintainer doesn't care about these things
|
||||
["commit", "<current-commit-id>"],
|
||||
["parent-commit", "<parent-commit-id>"],
|
||||
["commit-pgp-sig", "-----BEGIN PGP SIGNATURE-----..."], // empty string for unsigned commit
|
||||
["committer", "<name>", "<email>", "<timestamp>", "<timezone offset in minutes>"],
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Issues
|
||||
|
||||
Issues are Markdown text that is just human-readable conversational threads related to the repository: bug reports, feature requests, questions or comments of any kind. Like patches, these SHOULD be sent to the relays specified in that repository's announcement event's `"relays"` tag.
|
||||
|
||||
```jsonc
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 1621,
|
||||
"content": "<markdown text>",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["a", "30617:<base-repo-owner-pubkey>:<base-repo-id>"],
|
||||
["p", "<repository-owner>"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Replies
|
||||
|
||||
Replies are also Markdown text. The difference is that they MUST be issued as replies to either a `kind:1621` _issue_ or a `kind:1617` _patch_ event. The threading of replies and patches should follow NIP-10 rules.
|
||||
|
||||
```jsonc
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 1622,
|
||||
"content": "<markdown text>",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["a", "30617:<base-repo-owner-pubkey>:<base-repo-id>", "<relay-url>"],
|
||||
["e", "<issue-or-patch-id-hex>", "", "root"],
|
||||
|
||||
// other "e" and "p" tags should be applied here when necessary, following the threading rules of NIP-10
|
||||
["p", "<patch-author-pubkey-hex>", "", "mention"],
|
||||
["e", "<previous-reply-id-hex>", "", "reply"],
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Possible things to be added later
|
||||
|
||||
- "status" kind (for letting people know a patch was merged or an issue was fixed or won't be fixed)
|
||||
- "branch merge" kind (specifying a URL from where to fetch the branch to be merged)
|
||||
- "cover letter" kind (to which multiple patches can refer and serve as a unifying layer to them)
|
||||
- inline file comments kind (we probably need one for patches and a different one for merged files)
|
||||
260
46.md
260
46.md
@@ -1,222 +1,98 @@
|
||||
# NIP-46 - Nostr Remote Signing
|
||||
NIP-46
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
## Rationale
|
||||
Nostr Connect
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Private keys should be exposed to as few systems - apps, operating systems, devices - as possible as each system adds to the attack surface.
|
||||
`draft` `optional`
|
||||
|
||||
This NIP describes a method for 2-way communication between a remote signer and a Nostr client. The remote signer could be, for example, a hardware device dedicated to signing Nostr events, while the client is a normal Nostr client.
|
||||
This NIP describes a method for 2-way communication between a **remote signer** and a normal Nostr client. The remote signer could be, for example, a hardware device dedicated to signing Nostr events, while the client is a normal Nostr client.
|
||||
|
||||
## Terminology
|
||||
## Signer Discovery
|
||||
|
||||
- **Local keypair**: A local public and private key-pair used to encrypt content and communicate with the remote signer. Usually created by the client application.
|
||||
- **Remote user pubkey**: The public key that the user wants to sign as. The remote signer has control of the private key that matches this public key.
|
||||
- **Remote signer pubkey**: This is the public key of the remote signer itself. This is needed in both `create_account` command because you don't yet have a remote user pubkey.
|
||||
The client always starts by generating a random key which is used to communicate with the signer, then it one of the methods below is used to allow the client to know what is the signer public key for the session and which relays to use.
|
||||
|
||||
All pubkeys specified in this NIP are in hex format.
|
||||
### Started by the signer (nsecBunker)
|
||||
|
||||
## Initiating a connection
|
||||
|
||||
To initiate a connection between a client and a remote signer there are a few different options.
|
||||
|
||||
### Direct connection initiated by remote signer
|
||||
|
||||
This is most common in a situation where you have your own nsecbunker or other type of remote signer and want to connect through a client that supports remote signing.
|
||||
|
||||
The remote signer would provide a connection token in the form:
|
||||
The remote signer generates a connection token in the form
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bunker://<remote-pubkey>?relay=<wss://relay-to-connect-on>&relay=<wss://another-relay-to-connect-on>&secret=<optional-secret-value>
|
||||
bunker://<hex-pubkey>?relay=wss://...&relay=wss://...&secret=<optional-secret>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This token is pasted into the client by the user and the client then uses the details to connect to the remote signer via the specified relay(s).
|
||||
The user copies that token and pastes it in the client UI somehow. Then the client can send events of kind `24133` to the specified relays and wait for responses from the remote signer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Direct connection initiated by the client
|
||||
### Started by the client
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, basically the opposite direction of the first case, the client provides a connection token (or encodes the token in a QR code) and the signer initiates a connection to the client via the specified relay(s).
|
||||
The client generates a QR code in the following form (URL-encoded):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
nostrconnect://<local-keypair-pubkey>?relay=<wss://relay-to-connect-on>&metadata=<json metadata in the form: {"name":"...", "url": "...", "description": "..."}>
|
||||
nostrconnect://<client-key-hex>?relay=wss://...&metadata={"name":"...", "url": "...", "description": "..."}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## The flow
|
||||
The signer scans the QR code and sends a `connect` message to the client in the specified relays.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Client creates a local keypair. This keypair doesn't need to be communicated to the user since it's largely disposable (i.e. the user doesn't need to see this pubkey). Clients might choose to store it locally and they should delete it when the user logs out.
|
||||
2. Client gets the remote user pubkey (either via a `bunker://` connection string or a NIP-05 login-flow; shown below)
|
||||
3. Clients use the local keypair to send requests to the remote signer by `p`-tagging and encrypting to the remote user pubkey.
|
||||
4. The remote signer responds to the client by `p`-tagging and encrypting to the local keypair pubkey.
|
||||
## Event payloads
|
||||
|
||||
### Example flow for signing an event
|
||||
Event payloads are [NIP-04](04.md)-encrypted JSON blobs that look like JSONRPC messages (their format is specified inside the `.content` of the event formats below).
|
||||
|
||||
- Remote user pubkey (e.g. signing as) `fa984bd7dbb282f07e16e7ae87b26a2a7b9b90b7246a44771f0cf5ae58018f52`
|
||||
- Local pubkey is `eff37350d839ce3707332348af4549a96051bd695d3223af4aabce4993531d86`
|
||||
Events sent by the client to the remote signer have the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Signature request
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 24133,
|
||||
"pubkey": "eff37350d839ce3707332348af4549a96051bd695d3223af4aabce4993531d86",
|
||||
"content": nip04({
|
||||
"id": <random_string>,
|
||||
"method": "sign_event",
|
||||
"params": [json_stringified(<{
|
||||
content: "Hello, I'm signing remotely",
|
||||
pubkey: "fa984bd7dbb282f07e16e7ae87b26a2a7b9b90b7246a44771f0cf5ae58018f52",
|
||||
// ...the rest of the event data
|
||||
}>)]
|
||||
}),
|
||||
"tags": [["p", "fa984bd7dbb282f07e16e7ae87b26a2a7b9b90b7246a44771f0cf5ae58018f52"]], // p-tags the remote user pubkey
|
||||
"pubkey": "<client-key-hex>"
|
||||
"kind": 24133,
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["p", "<signer-key-hex>"]
|
||||
],
|
||||
"content": "nip04_encrypted_json({id: <random-string>, method: <see-below>, params: [array_of_strings]})",
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Response event
|
||||
And the events the remote signer sends to the client have the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 24133,
|
||||
"pubkey": "fa984bd7dbb282f07e16e7ae87b26a2a7b9b90b7246a44771f0cf5ae58018f52",
|
||||
"content": nip04({
|
||||
"id": <random_string>,
|
||||
"result": json_stringified(<signed-event>)
|
||||
}),
|
||||
"tags": [["p", "eff37350d839ce3707332348af4549a96051bd695d3223af4aabce4993531d86"]], // p-tags the local keypair pubkey
|
||||
}
|
||||
```js
|
||||
"pubkey": "<signer-key-hex>"
|
||||
"kind": 24133,
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["p", "<client-key-hex>"]
|
||||
],
|
||||
"content": "nip04_encrypted_json({id: <request-id>, result: <string>, error: <reason-string>})",
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Diagram
|
||||
The signer key will always be the key of the user who controls the signer device.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
### Methods
|
||||
|
||||
## Request Events `kind: 24133`
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": <id>,
|
||||
"kind": 24133,
|
||||
"pubkey": <local_keypair_pubkey>,
|
||||
"content": <nip04(<request>)>,
|
||||
"tags": [["p", <remote_user_pubkey>]], // NB: in the `create_account` event, the remote signer pubkey should be `p` tagged.
|
||||
"created_at": <unix timestamp in seconds>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `content` field is a JSON-RPC-like message that is [NIP-04](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/blob/master/04.md) encrypted and has the following structure:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": <random_string>,
|
||||
"method": <method_name>,
|
||||
"params": [array_of_strings]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `id` is a random string that is a request ID. This same ID will be sent back in the response payload.
|
||||
- `method` is the name of the method/command (detailed below).
|
||||
- `params` is a positional array of string parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
### Methods/Commands
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the following are methods that the client sends to the remote signer.
|
||||
|
||||
| Command | Params | Result |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `connect` | `[<remote_user_pubkey>, <optional_secret>]` | "ack" |
|
||||
| `sign_event` | `[<json_stringified_event_to_sign>]` | `json_stringified(<signed_event>)` |
|
||||
| `ping` | `[]` | "pong" |
|
||||
| `get_relays` | `[]` | `json_stringified({<relay_url>: {read: <boolean>, write: <boolean>}})` |
|
||||
| `get_public_key` | `[]` | `<hex-pubkey>` |
|
||||
| `nip04_encrypt` | `[<third_party_pubkey>, <plaintext_to_encrypt>]` | `<nip04_ciphertext>` |
|
||||
| `nip04_decrypt` | `[<third_party_pubkey>, <nip04_ciphertext_to_decrypt>]` | `<plaintext>` |
|
||||
| `nip44_encrypt` | `[<third_party_pubkey>, <plaintext_to_encrypt>]` | `<nip44_ciphertext>` |
|
||||
| `nip44_decrypt` | `[<third_party_pubkey>, <nip44_ciphertext_to_decrypt>]` | `<plaintext>` |
|
||||
|
||||
## Response Events `kind:24133`
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": <id>,
|
||||
"kind": 24133,
|
||||
"pubkey": <remote_signer_pubkey>,
|
||||
"content": <nip04(<response>)>,
|
||||
"tags": [["p", <local_keypair_pubkey>]],
|
||||
"created_at": <unix timestamp in seconds>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `content` field is a JSON-RPC-like message that is [NIP-04](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/blob/master/04.md) encrypted and has the following structure:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": <request_id>,
|
||||
"result": <results_string>,
|
||||
"error": <error_string>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `id` is the request ID that this response is for.
|
||||
- `results` is a string of the result of the call (this can be either a string or a JSON stringified object)
|
||||
- `error` is an error in string form.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auth Challenges
|
||||
|
||||
An Auth Challenge is a response that a remote signer can send back when it needs the user to authenticate via other means. This is currently used in the OAuth-like flow enabled by signers like [Nsecbunker](https://github.com/kind-0/nsecbunkerd/). The response `content` object will take the following form:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": <request_id>,
|
||||
"result": "auth_url",
|
||||
"error": <URL_to_display_to_end_user>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Clients should display (in a popup or new tab) the URL from the `error` field and then subscribe/listen for another response from the remote signer (reusing the same request ID). This event will be sent once the user authenticates in the other window (or will never arrive if the user doesn't authenticate). It's also possible to add a `redirect_uri` url parameter to the auth_url, which is helpful in situations when a client cannot open a new window or tab to display the auth challenge.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example event signing request with auth challenge
|
||||
|
||||
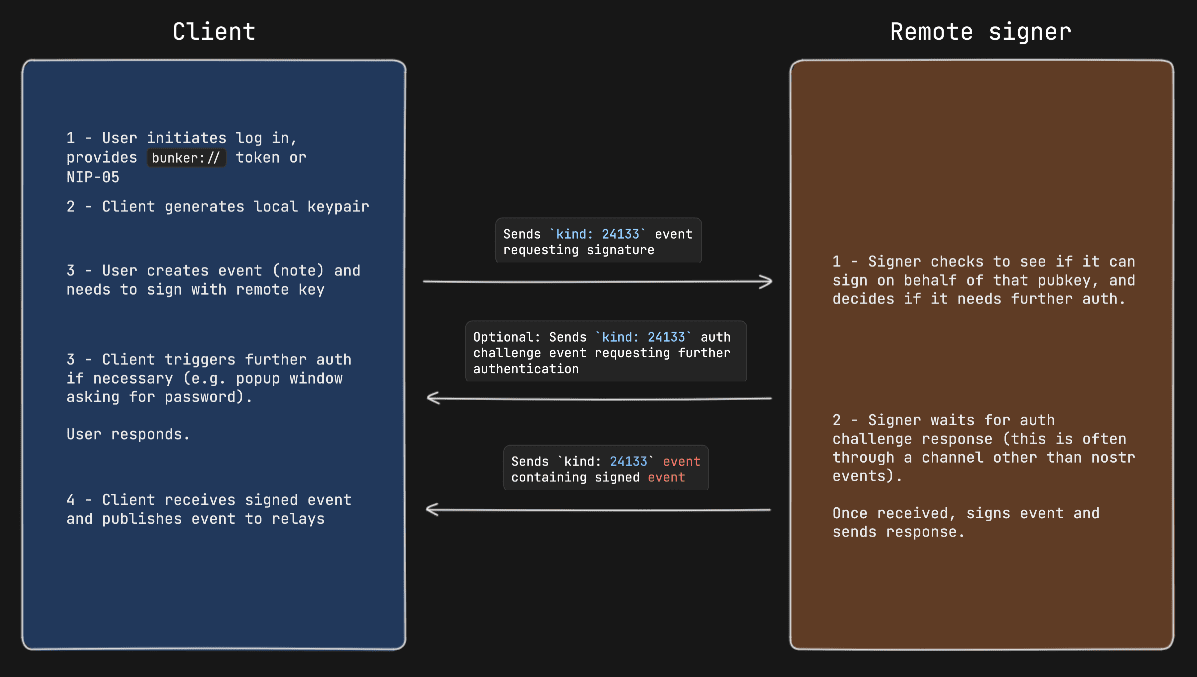
|
||||
|
||||
## Remote Signer Commands
|
||||
|
||||
Remote signers might support additional commands when communicating directly with it. These commands follow the same flow as noted above, the only difference is that when the client sends a request event, the `p`-tag is the pubkey of the remote signer itself and the `content` payload is encrypted to the same remote signer pubkey.
|
||||
|
||||
### Methods/Commands
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the following are methods that the client sends to the remote signer.
|
||||
|
||||
| Command | Params | Result |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `create_account` | `[<username>, <domain>, <optional_email>]` | `<newly_created_remote_user_pubkey>` |
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix
|
||||
|
||||
### NIP-05 Login Flow
|
||||
|
||||
Clients might choose to present a more familiar login flow, so users can type a NIP-05 address instead of a `bunker://` string.
|
||||
|
||||
When the user types a NIP-05 the client:
|
||||
|
||||
- Queries the `/.well-known/nostr.json` file from the domain for the NIP-05 address provided to get the user's pubkey (this is the **remote user pubkey**)
|
||||
- In the same `/.well-known/nostr.json` file, queries for the `nip46` key to get the relays that the remote signer will be listening on.
|
||||
- Now the client has enough information to send commands to the remote signer on behalf of the user.
|
||||
|
||||
### OAuth-like Flow
|
||||
|
||||
#### Remote signer discovery via NIP-89
|
||||
|
||||
In this last case, most often used to fascilitate an OAuth-like signin flow, the client first looks for remote signers that have announced themselves via NIP-89 application handler events.
|
||||
|
||||
First the client will query for `kind: 31990` events that have a `k` tag of `24133`.
|
||||
|
||||
These are generally shown to a user, and once the user selects which remote signer to use and provides the remote user pubkey they want to use (via npub, pubkey, or nip-05 value), the client can initiate a connection. Note that it's on the user to select the remote signer that is actually managing the remote key that they would like to use in this case. If the remote user pubkey is managed on another remote signer, the connection will fail.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, it's important that clients validate that the pubkey of the announced remote signer matches the pubkey of the `_` entry in the `/.well-known/nostr.json` file of the remote signer's announced domain.
|
||||
|
||||
Clients that allow users to create new accounts should also consider validating the availability of a given username in the namespace of remote signer's domain by checking the `/.well-known/nostr.json` file for existing usernames. Clients can then show users feedback in the UI before sending a `create_account` event to the remote signer and receiving an error in return. Ideally, remote signers would also respond with understandable error messages if a client tries to create an account with an existing username.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example Oauth-like flow to create a new user account with Nsecbunker
|
||||
|
||||
Coming soon...
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
- [NIP-04 - Encryption](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/blob/master/04.md)
|
||||
- **connect**
|
||||
- params: [`pubkey`, `secret`]
|
||||
- result: `"ack"`
|
||||
- **get_public_key**
|
||||
- params: []
|
||||
- result: `pubkey-hex`
|
||||
- **sign_event**
|
||||
- params: [`event`]
|
||||
- result: `json_string(event_with_pubkey_id_and_signature)`
|
||||
- **get_relays**
|
||||
- params: []
|
||||
- result: `json_string({[url: string]: {read: boolean, write: boolean}})`
|
||||
- **nip04_encrypt**
|
||||
- params: [`third-party-pubkey`, `plaintext`]
|
||||
- result: `nip04-ciphertext`
|
||||
- **nip04_decrypt**
|
||||
- params: [`third-party-pubkey`, `nip04-ciphertext`]
|
||||
- result: `plaintext`
|
||||
- **nip44_get_key**
|
||||
- params: [`third-party-pubkey`]
|
||||
- result: `nip44-conversation-key`
|
||||
- **nip44_encrypt**
|
||||
- params: [`third-party-pubkey`, `plaintext`]
|
||||
- result: `nip44-ciphertext`
|
||||
- **nip44_decrypt**
|
||||
- params: [`third-party-pubkey`, `nip44-ciphertext`]
|
||||
- result: `plaintext`
|
||||
- **ping**
|
||||
- params: []
|
||||
- result: `"pong"`
|
||||
|
||||
34
49.md
34
49.md
@@ -12,17 +12,17 @@ This NIP defines a method by which clients can encrypt (and decrypt) a user's pr
|
||||
Symmetric Encryption Key derivation
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
PASSWORD = Read from the user. The password should be unicode normalized to NFKC format to ensure that the password can be entered identically on other computers/clients.
|
||||
PASSWORD = read from the user
|
||||
|
||||
LOG\_N = Let the user or implementer choose one byte representing a power of 2 (e.g. 18 represents 262,144) which is used as the number of rounds for scrypt. Larger numbers take more time and more memory, and offer better protection:
|
||||
|
||||
| LOG_N | MEMORY REQUIRED | APPROX TIME ON FAST COMPUTER |
|
||||
|-------|-----------------|----------------------------- |
|
||||
| 16 | 64 MiB | 100 ms |
|
||||
| 18 | 256 MiB | |
|
||||
| 20 | 1 GiB | 2 seconds |
|
||||
| 21 | 2 GiB | |
|
||||
| 22 | 4 GiB | |
|
||||
| LOG\_N | MEMORY REQUIRED | APPROX TIME ON FAST COMPUTER |
|
||||
|--------|-----------------|----------------------------- |
|
||||
| 16 | 64 MiB | 100 ms |
|
||||
| 18 | 256 MiB | |
|
||||
| 20 | 1 GiB | 2 seconds |
|
||||
| 21 | 2 GiB | |
|
||||
| 22 | 4 GiB | |
|
||||
|
||||
SALT = 16 random bytes
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -78,22 +78,6 @@ The decryption process operates in the reverse.
|
||||
Test Data
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
## Password Unicode Normalization
|
||||
|
||||
The following password input: "ÅΩẛ̣"
|
||||
- Unicode Codepoints: U+212B U+2126 U+1E9B U+0323
|
||||
- UTF-8 bytes: [0xE2, 0x84, 0xAB, 0xE2, 0x84, 0xA6, 0xE1, 0xBA, 0x9B, 0xCC, 0xA3]
|
||||
|
||||
Should be converted into the unicode normalized NFKC format prior to use in scrypt: "ÅΩẛ̣"
|
||||
- Unicode Codepoints: U+00C5 U+03A9 U+1E69
|
||||
- UTF-8 bytes: [0xC3, 0x85, 0xCE, 0xA9, 0xE1, 0xB9, 0xA9]
|
||||
|
||||
## Encryption
|
||||
|
||||
The encryption process is non-deterministic due to the random nonce.
|
||||
|
||||
## Decryption
|
||||
|
||||
The following encrypted private key:
|
||||
|
||||
`ncryptsec1qgg9947rlpvqu76pj5ecreduf9jxhselq2nae2kghhvd5g7dgjtcxfqtd67p9m0w57lspw8gsq6yphnm8623nsl8xn9j4jdzz84zm3frztj3z7s35vpzmqf6ksu8r89qk5z2zxfmu5gv8th8wclt0h4p`
|
||||
@@ -102,6 +86,8 @@ When decrypted with password='nostr' and log_n=16 yields the following hex-encod
|
||||
|
||||
`3501454135014541350145413501453fefb02227e449e57cf4d3a3ce05378683`
|
||||
|
||||
The reverse process is non-deterministic due to the random nonce.
|
||||
|
||||
Discussion
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4
50.md
4
50.md
@@ -47,7 +47,3 @@ Relays SHOULD exclude spam from search results by default if they support some f
|
||||
|
||||
Relay MAY support these extensions:
|
||||
- `include:spam` - turn off spam filtering, if it was enabled by default
|
||||
- `domain:<domain>` - include only events from users whose valid nip05 domain matches the domain
|
||||
- `language:<two letter ISO 639-1 language code>` - include only events of a specified language
|
||||
- `sentiment:<negative/neutral/positive>` - include only events of a specific sentiment
|
||||
- `nsfw:<true/false>` - include or exclude nsfw events (default: true)
|
||||
|
||||
26
51.md
26
51.md
@@ -29,7 +29,6 @@ For example, _mute list_ can contain the public keys of spammers and bad actors
|
||||
| Public chats | 10005 | [NIP-28](28.md) chat channels the user is in | `"e"` (kind:40 channel definitions) |
|
||||
| Blocked relays | 10006 | relays clients should never connect to | `"relay"` (relay URLs) |
|
||||
| Search relays | 10007 | relays clients should use when performing search queries | `"relay"` (relay URLs) |
|
||||
| Simple groups | 10009 | [NIP-29](29.md) groups the user is in | `"group"` ([NIP-29](29.md) group ids + mandatory relay URL) |
|
||||
| Interests | 10015 | topics a user may be interested in and pointers | `"t"` (hashtags) and `"a"` (kind:30015 interest set) |
|
||||
| Emojis | 10030 | user preferred emojis and pointers to emoji sets | `"emoji"` (see [NIP-30](30.md)) and `"a"` (kind:30030 emoji set) |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,7 +49,6 @@ Aside from their main identifier, the `"d"` tag, sets can optionally have a `"ti
|
||||
| Curation sets | 30005 | groups of videos picked by users as interesting and/or belonging to the same category | `"a"` (kind:34235 videos) |
|
||||
| Interest sets | 30015 | interest topics represented by a bunch of "hashtags" | `"t"` (hashtags) |
|
||||
| Emoji sets | 30030 | categorized emoji groups | `"emoji"` (see [NIP-30](30.md)) |
|
||||
| Release artifact sets | 30063 | groups of files of a software release | `"e"` (kind:1063 [file metadata](94.md) events), `"i"` (application identifier, typically reverse domain notation), `"version"` |
|
||||
|
||||
## Deprecated standard lists
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -105,30 +103,6 @@ Some clients have used these lists in the past, but they should work on transiti
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A _release artifact set_ of an Example App
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "567b41fc9060c758c4216fe5f8d3df7c57daad7ae757fa4606f0c39d4dd220ef",
|
||||
"pubkey": "d6dc95542e18b8b7aec2f14610f55c335abebec76f3db9e58c254661d0593a0c",
|
||||
"created_at": 1695327657,
|
||||
"kind": 30063,
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["d", "ak8dy3v7"],
|
||||
["i", "com.example.app"],
|
||||
["version", "0.0.1"],
|
||||
["title", "Example App"],
|
||||
["image", "http://cdn.site/p/com.example.app/icon.png"],
|
||||
["e", "d78ba0d5dce22bfff9db0a9e996c9ef27e2c91051de0c4e1da340e0326b4941e"], // Windows exe
|
||||
["e", "f27e2c91051de0c4e1da0d5dce22bfff9db0a9340e0326b4941ed78bae996c9e"], // MacOS dmg
|
||||
["e", "9d24ddfab95ba3ff7c03fbd07ad011fff245abea431fb4d3787c2d04aad02332"], // Linux AppImage
|
||||
["e", "340e0326b340e0326b4941ed78ba340e0326b4941ed78ba340e0326b49ed78ba"] // PWA
|
||||
],
|
||||
"content": "Example App is a decentralized marketplace for apps",
|
||||
"sig": "a9a4e2192eede77e6c9d24ddfab95ba3ff7c03fbd07ad011fff245abea431fb4d3787c2d04aad001cb039cb8de91d83ce30e9a94f82ac3c5a2372aa1294a96bd"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Encryption process pseudocode
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
|
||||
55
64.md
55
64.md
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
||||
NIP-64
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Inbox model
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
`draft` `optional`
|
||||
|
||||
Suppose **Sarah** wants to subscribe to the notes **Walter** writes.
|
||||
|
||||
She must let Walter know she is following him. The first step is to find Walter's _inbox list_:
|
||||
|
||||
```jsonc
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 10064,
|
||||
"pubkey": "<walter>",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["relay", "wss://walter.inbox"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now Sarah can publish a `kind:6401` _follow intent_ to `wss://walter.inbox` tagging Walter:
|
||||
|
||||
```jsonc
|
||||
{
|
||||
"kind": 6401,
|
||||
"pubkey": "<sarah>"
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
["p", "<walter>"],
|
||||
["relay", "wss://sarah.inbox"],
|
||||
["relay", "wss://other.inbox"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sarah also publishes these to her own inbox relays (`wss://sarah.inbox` and `wss://other.inbox`) so they are aware.
|
||||
|
||||
From the Walter side, whenever he is about to publish a note, he downloads all the `kind:6401` events from his inbox relays and sends his note to all the relays he finds in these.
|
||||
|
||||
Whenever Sarah's inbox relay receive a note from Walter, they will know that Sarah is following him, so they index that note in a way that it is associated with Sarah. If the relays receive a note from someone else they can simply reject the note.
|
||||
|
||||
When Sarah turns on her client she will connect to her inbox relay, perform [NIP-42](42.md) `AUTH` and create a subscription that doesn't specify `"authors"` (for example, `["REQ", "_", {}]`). The relays, aware of who she is and who she is following, can deliver to her just Walter's notes.
|
||||
|
||||
If Sarah ever decides to stop following Walter, she just sends a `kind:5` _deletion_ to both Walter's relay and hers.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The approach described in this NIP doesn't replace any of the other models for following people that are already in use in Nostr, and doesn't claim to be strictly superior to the Outbox Model, but just provides an alternative way to do things.
|
||||
|
||||
In reality, clients should implement both approaches and can never assume others will implement this.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if Sarah wanted to follow Wesley and he didn't have a `kind:10064` she would have to do the normal "outbox" approach of subscribing to his relays and fetching his notes from there.
|
||||
|
||||
In the same vein, if for any reason Sarah noticed that she had stopped receiving notes from Walter for a long time (~7 days) it would make sense for her to go to his relays (obtained from [NIP-65](65.md), [NIP-05](05.md), relay hints or other means) and check if he is publishing to these. In the affirmative case, she would turn Walter into an "outbox follow" instead of an "inbox follow".
|
||||
2
65.md
2
65.md
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ The `.content` is not used.
|
||||
["r", "wss://alicerelay.example.com"],
|
||||
["r", "wss://brando-relay.com"],
|
||||
["r", "wss://expensive-relay.example2.com", "write"],
|
||||
["r", "wss://nostr-relay.example.com", "read"]
|
||||
["r", "wss://nostr-relay.example.com", "read"],
|
||||
],
|
||||
"content": "",
|
||||
...other fields
|
||||
|
||||
2
92.md
2
92.md
@@ -41,5 +41,3 @@ after the file is uploaded and included in the post.
|
||||
|
||||
When pasting URLs during post composition, the client MAY download the file
|
||||
and add this metadata before the post is sent.
|
||||
|
||||
The client MAY ignore `imeta` tags that do not match the URL in the event content.
|
||||
|
||||
46
BREAKING.md
46
BREAKING.md
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
This is a history of NIP changes that potentially break pre-existing implementations, in
|
||||
reverse chronological order.
|
||||
|
||||
| Date | Commit | NIP | Change |
|
||||
| ----------- | --------- | -------- | ------ |
|
||||
| 2024-02-25 | [4a171cb0](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/4a171cb0) | [NIP-18](18.md) | quote repost should use `q` tag |
|
||||
| 2024-02-16 | [cbec02ab](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/cbec02ab) | [NIP-49](49.md) | Password first normalized to NFKC |
|
||||
| 2024-02-15 | [afbb8dd0](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/afbb8dd0) | [NIP-39](39.md) | PGP identity was removed |
|
||||
| 2024-02-07 | [d3dad114](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/d3dad114) | [NIP-46](46.md) | Connection token format was changed |
|
||||
| 2024-01-30 | [1a2b21b6](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/1a2b21b6) | [NIP-59](59.md) | 'p' tag became optional |
|
||||
| 2023-01-27 | [c2f34817](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/c2f34817) | [NIP-47](47.md) | optional expiration tag should be honored |
|
||||
| 2024-01-10 | [3d8652ea](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/3d8652ea) | [NIP-02](02.md) | list entries should be chronological |
|
||||
| 2024-01-10 | [3d8652ea](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/3d8652ea) | [NIP-51](51.md) | list entries should be chronological |
|
||||
| 2023-12-30 | [29869821](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/29869821) | [NIP-52](52.md) | 'name' tag was removed (use 'title' tag instead) |
|
||||
| 2023-12-27 | [17c67ef5](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/17c67ef5) | [NIP-94](94.md) | 'aes-256-gcm' tag was removed |
|
||||
| 2023-12-03 | [0ba45895](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/0ba45895) | [NIP-01](01.md) | WebSocket status code `4000` was replaced by 'CLOSED' message |
|
||||
| 2023-11-28 | [6de35f9e](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/6de35f9e) | [NIP-89](89.md) | 'client' tag value was changed |
|
||||
| 2023-11-20 | [7822a8b1](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/7822a8b1) | [NIP-51](51.md) | `kind: 30000` and `kind: 30001` were deprecated |
|
||||
| 2023-11-11 | [cbdca1e9](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/cbdca1e9) | [NIP-84](84.md) | 'range' tag was removed |
|
||||
| 2023-11-07 | [108b7f16](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/108b7f16) | [NIP-01](01.md) | 'OK' message must have 4 items |
|
||||
| 2023-10-17 | [cf672b76](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/cf672b76) | [NIP-03](03.md) | 'block' tag was removed |
|
||||
| 2023-09-29 | [7dc6385f](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/7dc6385f) | [NIP-57](57.md) | optional 'a' tag was included in `zap receipt` |
|
||||
| 2023-08-21 | [89915e02](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/89915e02) | [NIP-11](11.md) | 'min_prefix' was removed |
|
||||
| 2023-08-20 | [37c4375e](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/37c4375e) | [NIP-01](01.md) | replaceable events with same timestamp should be retained event with lowest id |
|
||||
| 2023-08-15 | [88ee873c](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/88ee873c) | [NIP-15](15.md) | 'countries' tag was renamed to 'regions' |
|
||||
| 2023-08-14 | [72bb8a12](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/72bb8a12) | [NIP-12](12.md) | NIP-12, 16, 20 and 33 were merged into NIP-01 |
|
||||
| 2023-08-14 | [72bb8a12](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/72bb8a12) | [NIP-16](16.md) | NIP-12, 16, 20 and 33 were merged into NIP-01 |
|
||||
| 2023-08-14 | [72bb8a12](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/72bb8a12) | [NIP-20](20.md) | NIP-12, 16, 20 and 33 were merged into NIP-01 |
|
||||
| 2023-08-14 | [72bb8a12](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/72bb8a12) | [NIP-33](33.md) | NIP-12, 16, 20 and 33 were merged into NIP-01 |
|
||||
| 2023-08-11 | [d87f8617](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/d87f8617) | [NIP-25](25.md) | empty `content` should be considered as "+" |
|
||||
| 2023-08-01 | [5d63b157](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/5d63b157) | [NIP-57](57.md) | 'zap' tag was changed |
|
||||
| 2023-07-15 | [d1814405](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/d1814405) | [NIP-01](01.md) | `since` and `until` filters should be `since <= created_at <= until` |
|
||||
| 2023-07-12 | [a1cd2bd8](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/a1cd2bd8) | [NIP-25](25.md) | custom emoji was supported |
|
||||
| 2023-06-18 | [83cbd3e1](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/83cbd3e1) | [NIP-11](11.md) | 'image' was renamed to 'icon' |
|
||||
| 2023-04-13 | [bf0a0da6](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/bf0a0da6) | [NIP-15](15.md) | different NIP was re-added as NIP-15 |
|
||||
| 2023-04-09 | [fb5b7c73](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/fb5b7c73) | [NIP-15](15.md) | NIP-15 was merged into NIP-01 |
|
||||
| 2023-03-15 | [e1004d3d](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/commit/e1004d3d) | [NIP-19](19.md) | `1: relay` was changed to optionally |
|
||||
|
||||
Breaking changes prior to 2023-03-01 are not yet documented.
|
||||
|
||||
## NOTES
|
||||
|
||||
- If it isn't clear that a change is breaking or not, we list it.
|
||||
- The date is the date it was merged, not necessarily the date of the commit.
|
||||
32
README.md
32
README.md
@@ -15,7 +15,6 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
- [Criteria for acceptance of NIPs](#criteria-for-acceptance-of-nips)
|
||||
- [Is this repository a centralizing factor?](#is-this-repository-a-centralizing-factor)
|
||||
- [How this repository works](#how-this-repository-works)
|
||||
- [Breaking Changes](#breaking-changes)
|
||||
- [License](#license)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
@@ -45,11 +44,9 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
- [NIP-26: Delegated Event Signing](26.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-27: Text Note References](27.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-28: Public Chat](28.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-29: Relay-based Groups](29.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-30: Custom Emoji](30.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-31: Dealing with Unknown Events](31.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-32: Labeling](32.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-34: `git` stuff](34.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-36: Sensitive Content](36.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-38: User Statuses](38.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-39: External Identities in Profiles](39.md)
|
||||
@@ -81,6 +78,7 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
- [NIP-96: HTTP File Storage Integration](96.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-98: HTTP Auth](98.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-99: Classified Listings](99.md)
|
||||
- [NIP-302: Relay Pools](302.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Event Kinds
|
||||
| kind | description | NIP |
|
||||
@@ -94,11 +92,6 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
| `6` | Repost | [18](18.md) |
|
||||
| `7` | Reaction | [25](25.md) |
|
||||
| `8` | Badge Award | [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `9` | Group Chat Message | [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `10` | Group Chat Threaded Reply | [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `11` | Group Thread | [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `12` | Group Thread Reply | [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `13` | Seal | [59](59.md) |
|
||||
| `16` | Generic Repost | [18](18.md) |
|
||||
| `40` | Channel Creation | [28](28.md) |
|
||||
| `41` | Channel Metadata | [28](28.md) |
|
||||
@@ -108,12 +101,8 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
| `1021` | Bid | [15](15.md) |
|
||||
| `1022` | Bid confirmation | [15](15.md) |
|
||||
| `1040` | OpenTimestamps | [03](03.md) |
|
||||
| `1059` | Gift Wrap | [59](59.md) |
|
||||
| `1063` | File Metadata | [94](94.md) |
|
||||
| `1311` | Live Chat Message | [53](53.md) |
|
||||
| `1617` | Patches | [34](34.md) |
|
||||
| `1621` | Issues | [34](34.md) |
|
||||
| `1622` | Replies | [34](34.md) |
|
||||
| `1971` | Problem Tracker | [nostrocket][nostrocket] |
|
||||
| `1984` | Reporting | [56](56.md) |
|
||||
| `1985` | Label | [32](32.md) |
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +110,7 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
| `5000`-`5999` | Job Request | [90](90.md) |
|
||||
| `6000`-`6999` | Job Result | [90](90.md) |
|
||||
| `7000` | Job Feedback | [90](90.md) |
|
||||
| `9000`-`9030` | Group Control Events | [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `8000` | Relay Pool Join Request | [302](302.md) |
|
||||
| `9041` | Zap Goal | [75](75.md) |
|
||||
| `9734` | Zap Request | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
| `9735` | Zap | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
@@ -134,7 +123,6 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
| `10005` | Public chats list | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `10006` | Blocked relays list | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `10007` | Search relays list | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `10009` | User groups | [51](51.md), [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `10015` | Interests list | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `10030` | User emoji list | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `10096` | File storage server list | [96](96.md) |
|
||||
@@ -152,6 +140,7 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
| `30004` | Curation sets | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `30008` | Profile Badges | [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `30009` | Badge Definition | [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `30010` | Relay Pool | [302](302.md) |
|
||||
| `30015` | Interest sets | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `30017` | Create or update a stall | [15](15.md) |
|
||||
| `30018` | Create or update a product | [15](15.md) |
|
||||
@@ -160,20 +149,17 @@ They exist to document what may be implemented by [Nostr](https://github.com/nos
|
||||
| `30023` | Long-form Content | [23](23.md) |
|
||||
| `30024` | Draft Long-form Content | [23](23.md) |
|
||||
| `30030` | Emoji sets | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `30063` | Release artifact sets | [51](51.md) |
|
||||
| `30078` | Application-specific Data | [78](78.md) |
|
||||
| `30311` | Live Event | [53](53.md) |
|
||||
| `30315` | User Statuses | [38](38.md) |
|
||||
| `30402` | Classified Listing | [99](99.md) |
|
||||
| `30403` | Draft Classified Listing | [99](99.md) |
|
||||
| `30617` | Repository announcements | [34](34.md) |
|
||||
| `31922` | Date-Based Calendar Event | [52](52.md) |
|
||||
| `31923` | Time-Based Calendar Event | [52](52.md) |
|
||||
| `31924` | Calendar | [52](52.md) |
|
||||
| `31925` | Calendar Event RSVP | [52](52.md) |
|
||||
| `31989` | Handler recommendation | [89](89.md) |
|
||||
| `31990` | Handler information | [89](89.md) |
|
||||
| `39000-9` | Group metadata events | [29](29.md) |
|
||||
| `34550` | Community Definition | [72](72.md) |
|
||||
|
||||
[nostrocket]: https://github.com/nostrocket/NIPS/blob/main/Problems.md
|
||||
@@ -219,19 +205,18 @@ Please update these lists when proposing NIPs introducing new event kinds.
|
||||
| `l` | label, label namespace | annotations | [32](32.md) |
|
||||
| `L` | label namespace | -- | [32](32.md) |
|
||||
| `m` | MIME type | -- | [94](94.md) |
|
||||
| `q` | event id (hex) | relay URL | [18](18.md) |
|
||||
| `r` | a reference (URL, etc) | petname | |
|
||||
| `r` | relay url | marker | [65](65.md) |
|
||||
| `t` | hashtag | -- | |
|
||||
| `alt` | summary | -- | [31](31.md) |
|
||||
| `amount` | millisatoshis, stringified | -- | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
| `auth-required` | either nip-42 or nip-98 | -- | [302](302.md) |
|
||||
| `bolt11` | `bolt11` invoice | -- | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
| `challenge` | challenge string | -- | [42](42.md) |
|
||||
| `client` | name, address | relay URL | [89](89.md) |
|
||||
| `clone` | git clone URL | -- | [34](34.md) |
|
||||
| `content-warning` | reason | -- | [36](36.md) |
|
||||
| `delegation` | pubkey, conditions, delegation token | -- | [26](26.md) |
|
||||
| `description` | description | -- | [34](34.md), [57](57.md), [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `description` | invoice/badge description | -- | [57](57.md), [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `emoji` | shortcode, image URL | -- | [30](30.md) |
|
||||
| `encrypted` | -- | -- | [90](90.md) |
|
||||
| `expiration` | unix timestamp (string) | -- | [40](40.md) |
|
||||
@@ -240,7 +225,7 @@ Please update these lists when proposing NIPs introducing new event kinds.
|
||||
| `imeta` | inline metadata | -- | [92](92.md) |
|
||||
| `lnurl` | `bech32` encoded `lnurl` | -- | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
| `location` | location string | -- | [52](52.md), [99](99.md) |
|
||||
| `name` | name | -- | [34](34.md), [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `name` | badge name | -- | [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `nonce` | random | -- | [13](13.md) |
|
||||
| `preimage` | hash of `bolt11` invoice | -- | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
| `price` | price | currency, frequency | [99](99.md) |
|
||||
@@ -253,7 +238,6 @@ Please update these lists when proposing NIPs introducing new event kinds.
|
||||
| `summary` | article summary | -- | [23](23.md) |
|
||||
| `thumb` | badge thumbnail | dimensions in pixels | [58](58.md) |
|
||||
| `title` | article title | -- | [23](23.md) |
|
||||
| `web` | webpage URL | -- | [34](34.md) |
|
||||
| `zap` | pubkey (hex), relay URL | weight | [57](57.md) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Criteria for acceptance of NIPs
|
||||
@@ -278,10 +262,6 @@ Standards may emerge in two ways: the first way is that someone starts doing som
|
||||
|
||||
These two ways of standardizing things are supported by this repository. Although the second is preferred, an effort will be made to codify standards emerged outside this repository into NIPs that can be later referenced and easily understood and implemented by others -- but obviously as in any human system discretion may be applied when standards are considered harmful.
|
||||
|
||||
## Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
[Breaking Changes](BREAKING.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
All NIPs are public domain.
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user